Currently Empty: $0.00


All artificial sweeteners are not created equal
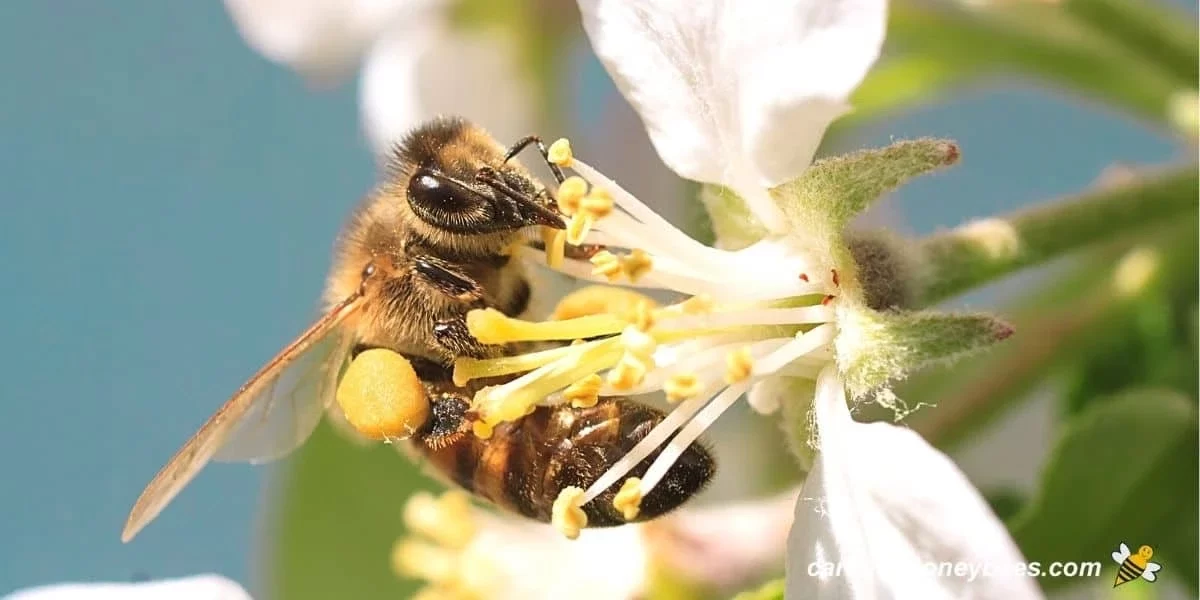
The FDA has approved five artificial sweeteners: saccharin, acesulfame, aspartame, neotame, and sucralose. It has also approved one natural low-calorie sweetener, stevia. How the human body and brain respond to these sweeteners is very complex.
One concern is that people who use artificial sweeteners may replace the lost calories through other sources, possibly offsetting weight loss or health benefits, says Dr. Ludwig. This can happen because we like to fool ourselves: “I’m drinking diet soda, so it’s okay to have cake.” The AHA and ADA also added this caveat to their recommendation.
It’s also possible that these products change the way we taste food. “Non-nutritive sweeteners are far more potent than table sugar and high-fructose corn syrup. A miniscule amount produces a sweet taste comparable to that of sugar, without comparable calories. Overstimulation of sugar receptors from frequent use of these hyper-intense sweeteners may limit tolerance for more complex tastes,” explains Dr. Ludwig. That means people who routinely use artificial sweeteners may start to find less intensely sweet foods, such as fruit, less appealing and unsweet foods, such as vegetables, downright unpalatable.
In other words, use of artificial sweeteners can make you shun healthy, filling, and highly nutritious foods while consuming more artificially flavored foods with less nutritional value.